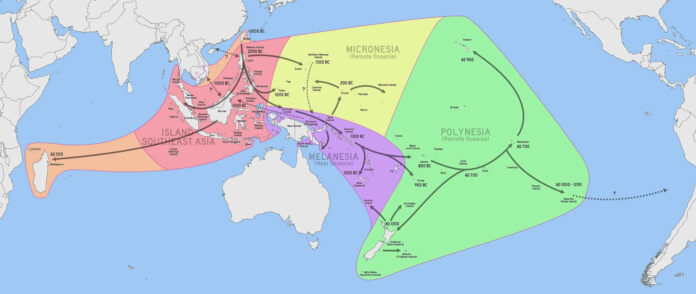
The Austronesian expansion was a major series of migrations undertaken by Austronesian-speaking peoples, beginning from Taiwan around 3000-1500 BC.
The expansion is considered one of the most significant migration events in human history, leading to the settlement of a vast area stretching from Madagascar to Easter Island, and as far north as Hawaii.
Origins
The origins of the Austronesian expansion are traced back to the island of Taiwan. From there, Austronesian-speaking peoples began to spread outwards, initially moving southwards to the Philippines and Indonesia.
The austronesian expansion is truly remarkable pic.twitter.com/Td56S5z1bB
— Jasper Gregory (@jaspergregory) March 9, 2019
Migration Patterns
The Austronesian expansion was characterized by two major migration routes:
- Western Route: This led to the settlement of the Philippines, eastern Indonesia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, and ultimately reaching as far west as Madagascar off the southeastern coast of Africa. This was a remarkable feat of oceanic navigation, as it involved crossing vast stretches of open ocean.
- Eastern Route: This route involved the colonization of the rest of the Pacific Islands, including Polynesia, New Zealand, and Hawaii. This expansion was marked by long ocean voyages across remote islands in the Pacific Ocean.
Impact and Significance
The importance and impact of the migration were:
Cultural Influence: The Austronesian expansion had a profound impact on the languages, cultures, and technologies of the regions it reached. Austronesian languages form one of the world’s largest language families, and the cultural practices and technologies of these peoples influenced many regions.
Nautical Technology: Austronesian peoples were skilled seafarers and navigators. They developed advanced sailing technologies, including outrigger canoes and sophisticated knowledge of wind and currents, which enabled them to undertake these extensive voyages.
Agricultural Practices: They also introduced new agricultural practices and crops, such as taro and yams, to the islands they settled, significantly impacting local economies and environments.
Genetic and Archaeological Evidence: The spread of the Austronesian peoples is well-documented through genetic, linguistic, and archaeological evidence, showing a remarkable spread of human populations and culture.
What is the available evidence of the Austronesian Expansion?
The origins of the Austronesian expansion can be traced back to the regions of Taiwan and Southeast Asia, with the most widely accepted theory suggesting that it began from Taiwan around 3000-1500 BC. This historical movement marks the spread of Austronesian-speaking peoples across vast oceanic regions, leading to the settlement of a wide area including Polynesia, Micronesia, Madagascar, and parts of Southeast Asia.
- Linguistic Evidence: The Austronesian language family, which is one of the largest in the world, shows its earliest roots in Taiwan. Linguistic studies suggest that the Proto-Austronesian language, the ancestor of all Austronesian languages, originated in Taiwan.
- Archaeological Findings: Archaeological evidence, including pottery, tools, and domesticated plants and animals, indicates that the early Austronesian peoples in Taiwan had developed agricultural and maritime technology that enabled them to undertake long sea voyages.
- Cultural and Genetic Exchange: As the Austronesian people expanded, they interacted with other cultures, leading to cultural and genetic exchanges. This is evidenced by the diverse cultural practices and linguistic variations across Austronesian-speaking populations.